Vitalia Acosta

“Learning is living, and you only live if you continue learning” Jose Maria Gasalla
The world changes second by second; therefore, education has been evolving. If we look back, we see that many things we have available today, such as technology, television programs, and books, thirty years ago did not exist; the culture of learning has been incorporated into society.
Culture is a critical component of the learning environment. It is essential to be aware of the influence that culture has on all learning environments and try to adapt that culture to support the type of environment that we believe will be most effective. However, changing a learning culture was challenging. However, new technologies allow you to create new learning environments and also allow you to create the type of culture that is most appropriate for your students.
(Thomas and Brown, 2011). It indicates that the fundamental difference between a teaching and a learning-based approach is that “in the first case, culture is the environment, while in the second, culture emerges and grows together with the environment.”.”
In every learning environment, cultural elements will dominate the other components of the environment. For this reason, I have considered culture to be the support for all other components of a learning environment.
The new learning culture is about adapting to changes and seeking new ways of learning through innovation, cultivating imagination, and learning by doing. According to Professor Douglas Thomas, its main objective is to seek a balance between institutional structure and individual freedom. New learning proposals and projects are emerging that use technological tools in non-traditional environments, as described in my Innovation Plan .
My innovation proposal will integrate Blended Learning in two languages in the technological field so that children from pre-kindergarten to 5th grade can opt for dual blended learning in the station rotation model.
Observing the advances and the use of some technological resources in the rotation of stations that facilitate empowerment and learning will improve the conditions for designing proposals that contemplate spaces and times from a dual logic. It will positively strengthen student learning; most importantly, students will be owners of their learning and time (according to their knowledge and interests). Create educational and technological platforms developed as new forms of interaction between teachers and students. Incorporating computational thinking into the curriculum will help us intentionally prepare them for the challenges ahead.
For more information on the research on blended learning, read my Literature Review
Hybrid and blended learning can show poor planning and increasing opportunities in uncertain times. Dependence. Productivity worsens.
Linking technology to teaching and learning does not mean dismissing the above comments. The ideal would be to incorporate, adapt, and create a new learning system by designing classrooms that better reflect the world in which students will participate once they graduate.
By allowing students to progress in their learning at their own pace, they begin to work on their knowledge, skills, values, and attitudes, enabled through study, teaching, or experience. This process can be understood from various positions, which implies that different theories are linked to learning.
We can use various methodologies to promote the learning of our students. As a teacher, I do not force my students to repeat what was taught in class. On the contrary, incentives to pay attention to details of the environment and to use creativity to build one's concepts, preparing to question reality.
When learning, they analyze and understand information from outside and apply it to their learning. They must forget prejudices and acquire new behavior. Learning forces them to change behavior and reflect new knowledge in present and future experiences.
It cannot be mentioned that the learning possibilities are multiplying thanks to innovation and the digital tools that exist today. Numerous educational platforms and resources are available with Internet access where supervised learning is effective.
The main objective is for my students to obtain reliable and individualized learning in two languages, facilitate communication, relationships, and knowledge of new cultures, and access information that does not encounter barriers to finding themselves in one language or another. I will give my students the power of their learning. I plan to achieve that goal by using Chromebooks and our learning management system within a flexible classroom environment with personalized attention.
Holism in the human area forces us to see the person differently than what we are culturally accustomed to; it is to see the person as a whole more significant than the sum of its parts. “The person is the integrated functioning of the various aspects of the whole in time and space.” (Kepner, 2000, p.36) Therefore, treating a single aspect of the person is, as Kepner says, artificially fragmenting what is actually found in a functioning unit. Holism views personal processes (conflicts, physical symptoms, traumas, etc.) as part of a greater whole, including physical and psychological aspects. “In terms of method, the holistic approach aims to bring together all aspects of the person so that they can experience themselves as a unitary organism rather than as a mixture of parts. From this position, the therapeutic technique should not split the person by paying attention to one aspect as if it were intrinsically different or separate from the other."
Education is one of the pillars of society. Through it, the human being discovers himself and the world around him, enriching his knowledge of it but acquiring the values that develop him as an individual. That is why taking care of education and considering the best possible paths to follow are necessary missions for a healthy society. Traditional education has contributed to this, but certain aspects question both its methods and effectiveness. This is what many students of all ages who are in their study stage believe.
Probably the main reason these “failures” are more evident is the passage of time. The traditional education system has remained unchanged while many changes have arisen. The development of the Internet, the emergence of new technologies, and even the evolution and change of people and their ways of relating to information. Traditional education seems to have turned its back on innovation precisely at the moment of the most significant information and knowledge revolution in all areas.
Within the standardized methods and habits we know, several voices propose criticism and reform accused of being erroneous. One of them would be the grading system. This could damage their personality and self-perception, it can be very damaging.
In the same way that they demotivate, the actual value of the knowledge acquired cannot be affirmed. This affects the aspects indicated and is the method of the student's interaction with knowledge. This is summarized in constant memorization and emptying of information, in which, many times, it is forgotten as soon as the student takes the exam. So, no learning occurs. On the other hand, this can truncate innovation: the one who accumulates the most knowledge and optimizes your performance, which is why conventional pedagogy is designed for memorization.
Another question is the lack of freedom of the student and the absence of stimulation of creativity. Everyone studies the same subjects under the exact expectations, without considering each student's peculiarities or talents. The programs, structured and without room for the student to appropriate them or leave their content, clip the wings of initiative and choice. As a consequence of not encouraging critical thinking or self-initiative, when the student receives a certain degree of freedom, he does not know what to do with it.
The format of the classes is also indicated—classrooms of 30 students dedicated to listening to a teacher's voice for long periods. There is vast theoretical content with very little practical application, a feeling of irrelevant information, and students are relegated to a strictly passive attitude. This destroys interest and passion, two fundamental catalysts in human learning.
References
Kepner, J. (2000). “Proceso corporal”. México D. F.: Manual Moderno.
https://www.understood.org/en/articles/growth-mindset
amazon.com/New-Culture-Learning-Cultivating-Imagination/dp/1456458884
A New Culture of Learning by Doug Thomas & John Seely Brown
(PDF) Digitization, Digitalization, and Digital Transformation (researchgate.net)
My Creating Learning
Philosophy

In this world of constant changes, the Philosophy of learning and the optimization of education plays a crucial role in the development and success of students. Education is not limited to classrooms but encompasses a comprehensive approach that seeks to enhance skills, knowledge, and competencies. Effective learning methods tailored to individual needs enable teachers to acquire and apply knowledge meaningfully, encouraging critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving.
Optimizing education is critical to preparing students for the challenges of the modern world and providing them with the tools necessary to reach their full potential. Learning theories are conceptual frameworks that seek to explain how students acquire, process, and retain knowledge.
Learning Philosophies can have a significant impact on education, as they provide theoretical bases to design more effective pedagogical strategies and promote optimal learning.
However, it is possible to identify three widely recognized and studied learning theories. Some well-known theories include "Behaviorism, Cognitivism, and Constructivism from a Critical Educational Design Perspective." Peggy A. Ertmer and Timothy J. Newby
Each of these theories brings a unique understanding of how learning occurs and how my students' educational processes can be optimized. It is important to note that these theories are often intertwined and complement each other to achieve the desired learning. Each learning theory offers us a unique perspective on how learning occurs; as teachers, we can design effective pedagogical strategies to benefit students. Analyze each learning perspective in terms of specific interpretation within the learning process and development of results that are effective for the education of my students.
Learning is a constant process, where the world is constantly changing every day, and we do not stop learning; through learning, skills, knowledge, behaviors, and values are acquired and developed. It is the result of attention, study, experience, instruction, reasoning, and observation, as well as the influence of factors with which we interact. Many times, it is a struggle and challenge that involves both experience and knowledge, not only on a personal but also professional level, acquired throughout life, at any age, in all contexts of life, and through different modalities and means or channels.
Often, a learning experience is a significant advancement, and other times, it is a minor event. I believe in the following aspects of learning that are valid regardless of the learning situation we obtain: Learning is a process that lasts a lifetime; we are constantly learning at every moment and everywhere.
As a student, my passion is learning; I am constantly learning. I have always loved school and learning, and I love learning new things; I do not want to stop learning. After 12 years of leaving a classroom, it has been a great challenge for me to start again with all the different study tools, language, class modality, and evaluation systems. I have already adapted to this new learning process. I look for my own experiences, and I constantly strive to improve myself in what I do. I am motivated to learn; I had to learn everything from scratch many times. I thought I could not, but I managed it. I am the owner of my learning; when I look back, I say I achieved it, but I still have much to learn. As a student, I am responsible for attending class and completing assignments as directed by the teacher. Many times, I need to be a very passive listener. The following is about my learning: I have to process information and talk about it. To foster a deeper level of understanding by actively engaging with the material or interacting with it in some way to achieve my goal. The learning and teaching strategies have strengthened the effectiveness and efficiency of my learning, ultimately allowing me to achieve my goals successfully.
On the other hand, my experience as a teaching student is to use critical thinking since it significantly improves the teaching-learning processes. Not only does it train my students to integrate the information-processing strategies I am teaching, but it also empowers them to retain the information they are receiving. Teaching critical thinking focuses on my students being able to process, think, and apply the information they receive. As a teacher, I will provide students with the necessary tools to become successful learners.
Moreover, these learning tools can be applied inside and outside the classroom, that is, in a wide variety of contexts. We will work together to create meaningful learning environments. This is just one of the variables that affect the teaching-learning process, which we will be reviewing within the learning theories. With this analysis, we want to begin a path toward integrative models capable of harmonizing the most significant number of principles in each, avoiding turbulence produced by their separate applications.
To conclude, improvements in the teaching-learning processes do not depend on sophisticated technologies but on pedagogical proposals supported by models that integrate them and demonstrate the best use of the technologies at our disposal to achieve quality education.
Behaviorism: Focuses on observable learning and the influence of the environment and external stimuli on the acquisition of behaviors.
Before understanding what the behavioral educational model entails, it must be clarified that learning is inherent to human beings. Therefore, each person learns differently. Sylwester (2008) states that human beings never stop learning throughout. In his life, Some people learn quickly while others learn easily; it all depends on knowing how they learn and applying the appropriate teaching methodology. In this statement, we can mention Beebe, Oyeyinka, Kouakou, and Rao. (2003), which says that knowledge opens the doors to more learning. Students must have learned in direct line with the needs and demands of society; that is, they must acquire skills that help them integrate and contribute to the development of the community, which is why social change must go hand in hand. Change curricular designs in a sense of continuous evolution, opening the possibility that not only the teacher changes his role but also that the student himself adopts his new function in this teaching-learning process of the new millennium.
In education, behaviorism has numerous applications, and its techniques are prevalent in the classroom to improve students' acquisition of knowledge and their behavior or attitude in class. It should be noted that behavioral learning follows a vertical communication model in which the teacher is placed above the student. The teacher assumes the role of an active sender who has to modify the behaviors of his students, and to do so; he must provide them with the appropriate stimuli at all times.
My tendencies regarding this behavior are centered within the classroom area. When my students have a hard time returning to the focus of the class, I tell them to raise their hands, and immediately, they are silent and in the correct position. Ivan P. Pavlov (1849-1936). He focuses on the study of observable behavior to control and predict it. His objective is to achieve a specific behavior to avoid negative consequences. I always seek to have good communication with my
In the same way, motivation consists of stimulating my students to put their faculties into activity. However, when applied correctly, reinforcement can successfully modify behavior and stimulate learning, but never the comprehensive training of the student.
As the Chinese philosopher Confucius said: "Learning without reflection is a waste of energy." It is a learning method that consists of several mental operations that are based on experience and the individual's processing of information from it in order to assimilate knowledge and give an answer in this way. In the mind, existing ideas are connected, that is, what one already knows, with new information to deepen memory and retention capacity. For example, association, which for Gagné (1979, 6) "is the simplest form of learned capabilities, and which constitutes the foundation of other more complex types of those same capabilities," went from a relationship between ideas to links between stimuli and responses. The primary distinction between the behaviorist and cognitivist currents lies in how knowledge is conceived. For behaviorism, knowledge consists mainly of a passive and automatic response to external environmental stimuli. Cognitivism considers knowledge basically as symbolic representations in the minds of individuals.
In this sense, my students not only relate to these factors but also process and store information related to these circumstances or actions, launching cognitive processes to complete learning. In classes, we use the cognitivist theory. I emphasize that they pay attention to memory, perception, recognition patterns, and the use of language in the learning process of my students. Then, for feedback, I use simple tools so that they have speed and good understanding. (Ertmer and Newby, 1993), Piaget (1964).
Each school year, I seek to improve my objective and goals as a teacher to improve my students' learning of how to learn and think better so that they can develop their skills and strengths and see their needs as a priority in their level of learning, which is a fundamental part of cognitivism.
Tan and Hung (2003) state that "learning is an active process of construction rather than acquisition of knowledge" (p. 49). According to the constructivist, it encourages the student to participate in the active process of meaning: construction in genuine and authentic problems and situations, and where students can socially construct knowledge with others. Seng Chee Tan and David Hung (2003)
Constructivism Jean Piaget 1952. It focuses on the process of knowledge construction and how the student is an active participant in this process. Constructivism assumes that nothing comes from nothing. Prior knowledge gives birth to new knowledge. Constructivism argues that learning is active. A person who learns something new incorporates it into their previous experiences and mental structures. Each new information is assimilated and deposited in a network of knowledge and experiences previously in the subject. As a result, learning is neither passive nor objective; on the contrary, it is a subjective process that each person constantly modifies at will—in light of their experiences (Abbott, 1999).
In summary, learning is an active process in which my students build knowledge every moment, motivating them and getting them to commit to their learning process. This can happen through hands-on and digital activities.
Bandura Social constructivism is that which occurs in contact with others and the environment; in the interaction that occurs between learning and the environment lies an excellent learning potential that, if it also converges with other individuals, can give rise to a type of much more consistent learning. However, social learning can also be understood as learning that arises thanks to interaction with other people, such as peer learning, where my students teach each other, helping each other and thus being easier. For many, the understanding of certain concepts.
The study of social learning is usually related to other concepts, such as cooperative learning, collaborative learning, or peer learning. What must be considered is that learning, when it is social, is much more effective, productive, and beneficial and that the human being is a primarily social being who needs others to grow. And develop. All human beings are born with a clear innate preference for social stimuli, and, in their first days, they need others to meet their needs and survive, a need that will continue throughout life.
Educators can be more likely to be successful if we understand that peer participation is critical to learning. Isolating learning is not the best way to help students learn and grow together. Progressive education recognizes that social interaction is key to learning and uses conversation, interaction, and group applications to help students retain their knowledge.
Connectivism, according to George Siemens (2005), is a learning theory for the digital age, which is based on the analysis of behaviorism, cognitivism, and constructivism to explain the effect that technology has had on the way that we currently live, communicate, and learn. It integrates the principles explored by the theories of chaos, networks, complexity, and self-organization. This focuses on including technology as part of our distribution of cognition and knowledge.
The combination of constructivist theories, social learning, and experiences has allowed me to. While students should develop their knowledge by establishing connections and engaging in experiences, they also need guidance and support from an educator or mentor. In general, My teaching philosophy is based on the conviction that my students learn more; it encourages them to be themselves in their learning process. I will be a guide in their learning; I analyze how I teach them, administer my classroom, and attend to the needs of each of my students. My teaching philosophy must match my learning philosophy. Everything learned in our class improves their understanding and gives them good performance in the future. These three learning theories described above influence my innovation plan and my role as a change agent in my school.
As part of my INNOVATION PLAN focuses on improving the blended learning environment in my classroom, I will focus less on emphasizing traditional assessments that are more behavioral in favor of performance assessments where students can participate in situations . . authentic, increasing their motivation and commitment. Blended learning allows students to take control of their learning, navigate content, interpret information freely, and move at their own pace.
Learning is individualized, and therefore, teaching should be personalized. The growth mindset is what allows me to advance day by day in my learning and plays a vital role in this process. Constructivist, social, and experiential learning theories are integrated into my blended learning initiative.
References
Dweck, Carol S (2006) Mindset: The new psychology of success.
Thomas, D., & Brown, J. S. (2011). A new culture of learning: Cultivating the imagination for a world of constant change. Lexington, KY: CreateSpace.
CAPITULO 2: ENSEÑANZA Y APRENDIZAJE (ó cap 4) (tdx.cat)
https://www.tdx.cat/bitstream/handle/10803/8927/D-TESIS_CAPITULO_2.pdf
https://epperu.org/teorias-del-aprendizaje/
Harapnuik, D. (2009, August 18). Inquisitivism. It's About Learning. Retrieved June 23, 2021, from http://www.harapnuik.org/?page_id=104
Harapnuik, D. (2016, March 11). Four keys to understanding learning theories. It's About Learning. Retrieved June 23, 2021, from http://www.harapnuik.org/?p=6344
Annotated Bibliography
Unesco. (2017). Most influential theories of learning. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. Retrieved from this source.
This publication provides an overview of several different learning theories: behavioral, cognitive, constructivist, experiential learning, multiple intelligence, situated learning, and community of practice. This was a great start to understand the different learning theories.
The following is a list of resources that I have learned from which have led to my beliefs on learning, although not cited in my learning philosophy.
Thomas, D., & Brown, J. S. (2011). A new culture of learning: Cultivating the imagination for a world of constant change. Lexington, KY: CreateSpace.
-Thomas and Brown discuss the need to incorporate passion, imagination, and constraint with play into the learning environment in order for children to learn in today’s ever-changing world.
Siemens, G. (2005). Connectivism: A learning theory for the digital age. International Journal of Instructional Technology and Distance Learning, 2(1), 3-10. Retrieved from http://www.itdl.org/journal/jan_05/Jan_05.pdf
-George Siemens looks at connectivism theory, which is related to constructivism, and its impact in the digital age and on 21st century learners.
Harapnuik, D. (2009, August 18). Inquisitivism. It's About Learning. Retrieved June 23, 2021, from http://www.harapnuik.org/?page_id=104
Dr. Harapnuik describes an evolving new and unique learning theory called inquisitism that is used throughout online courses. The two main focuses of inquisitivism are the removal of fear and the stimulation of inquisitive nature.
Harapnuik, D. (2016, March 11). Four keys to understanding learning theories. It's About Learning. Retrieved June 23, 2021, from http://www.harapnuik.org/?p=6344
Harapnuik uses four key points in describing and explaining why learning theories are important to understand.
National Research Council. (2000). Inquiry and the national science education standards: A guide for teaching and learning. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
-Although almost 20 years old, the book focuses on the relevant information that students learn through inquiry and guides teachers through the use of inquiry in the classroom.
Piaget, J. (1964). Part I: Cognitive development in children: Piaget. Journal of Research in Science Education, 2, 176-186.
-Piaget, Talk about cognitive development since this involves changes in the child's ability to reason about the world.
Dweck, C. S. (2006). Mindset: The new psychology of success. New York: Random House.
-Dweck explores the power that having a growth mindset can have on success. The growth mindset has implications in teaching and learning.


Aligning Outcomes, Activities, and Assessments
Outcomes, activities, and assessments must be aligned when creating meaningful learning environments. To achieve this goal, education must have significant characteristics, where the role of teachers is to appropriate the necessary elements so that the student is the protagonist, not only in his or her learning but also able to interact with others. An intentional, planned, and systematic educational process is required, which takes into account the individual differences, interests, needs, and problems of each student to harmonize what the education of the school system aims for and the motivations. . specific to each individual, not just providing content, we should focus on connecting dots, allowing our students to establish connections with their learning (Godin, 2012). Outcomes, activities, and assessments must be aligned regarding fundamental knowledge, application, integration, human/caring dimension, and learning how to learn (Fink, n.d.)
Furthermore, the role of the teacher in meaningful learning leads the student to build significant knowledge in authentic environments and develop connections, considering their social environment and based on the aptitudes and attitudes that strengthen their knowledge systems, skills, and values. To create lifelong learners.
Using the guide Fink (2003) created, I developed a plan for my class. I started with BHAG, the Big Hairy Audacious Goal; the first step to planning is to focus on my INNOVATION PLAN. Creating the BHAG first allowed me to keep my end goal in sight and focus all outcomes, activities, and assessments on that to design a unit. Cohesive with vital goals where my students can learn and connect in an engaging, student-centered environment. All learning elements are linked to Fink's model of meaningful learning.
Thinking behind the 3 column table:
BHAG: Participating teachers, applying their learning expertise, seek to help students use a specific range of skills to learn curriculum content or complete other tasks efficiently and effectively. Encourage students to be creative and authentic, listening, speaking, reading, and writing, in a blended learning environment so they are successful throughout the school year and beyond.


References
Fink, L. D. (2005). A self-directed guide to designing courses for significant learning. Retrieved from: https://www.deefinkandassociates.com/GuidetoCourseDesignAug05.pdf
Godin, S. [TEDxYouth]. (2012, October 16). Stop stealing dreams [video]. Retrieved from [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sXpbONjV1Jc]
Harapnuik, D. (2015, August 15). Connecting the dots vs. collecting the dots [Video file]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=1&v=85XpexQy68g
Resources
Learning How to Learn:
Develop assignments for students for EP publication?
Design 3 Column Tables for specific units in our classrooms?
A New Culture of Learning
Human Dimension:
Sinek’s Why
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qp0HIF3SfI4
Munster TechLabs
A New Culture of Learning
Foundational:
What is and EP
http://www.harapnuik.org/?page_id=5977
Understanding By Design Template
The UbD Template emphasizes the importance of setting goals because long-term goals are the difference between knowing and understanding. Wiggins and McTighe (2005) design framework is taken from Understanding by Design by Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe. Here, I leave you the design of my dual language blended learning plan, which I will present this year.
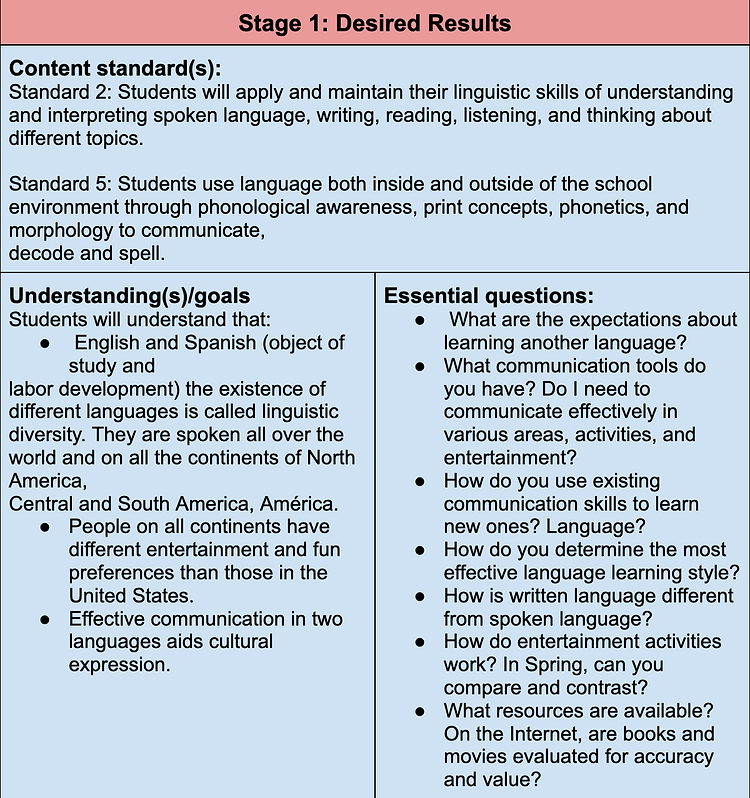




W = Make sure students understand WHERE the unit is going and WHY.
H = ENGAGE students at the beginning and KEEP their attention throughout.
E = EQUIP students with the experiences, tools, knowledge, and expertise necessary to achieve performance goals.
R = Provide students with numerous opportunities to RETHINK big ideas, REFLECT on progress, and REVIEW their work.
E = Build opportunities for students to EVALUATE progress and self-evaluate.
T = Be PERSONALIZED to reflect individual talents, interests, styles and needs.
O = Be ORGANIZED to optimize deep understanding rather than superficial coverage.
References
Fink, L. D. (2003). A Self-Directed Guide to Designing Courses for Significant
Learning. Creating Significant Learning Experiences: An Integrated Approach to
Designing College Courses. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Wiggins, G. P., & McTighe, J. (2008). Understanding by design (2nd ed.). Alexandria, Va.: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development
Growth Mindset Plan & Final Compilation
The world changes second by second; Therefore, education has been evolving. Looking back, we see that many things available today, such as technology, television shows, and books, did not exist thirty years ago. The culture of learning has been incorporated into society.
The way has been opened to various innovative practices and methods that aim to improve the teaching structures of the past. This will benefit authentic learning, where my students feel more engaged and motivated to learn when they address real-world problems that interest them. And as a result, they remember what they have learned and can apply it more effectively in the future. I invite you to see my INNOVATION PLAN.
In particular, CSEL by incorporating blended learning and new technologies, adapts to changes and seeks new ways of learning through innovation, cultivates imagination, and learns by doing NEW CULTURE.
Creating MY LEARNING PHILOSOPHY is having an open mind, a positive attitude, and high expectations in the classroom every day, focusing on two fundamental aspects: the nature of learning and the purpose of education. I seek to help my students develop the knowledge, skills, and academic habits that will lead them to success in life.
In this scenario, we are convinced that one of the fundamental roles that must be fulfilled is to transmit what one knows and guide students to discover a universe of meanings and learning they had never imagined. Call to Action Education is in motion, inviting us to rethink ourselves to find our motivation to continue learning. THE 3 COLUMN TABLE and the UBD DESIGN will help me gain knowledge and skills for my individual and professional development.
Using the five principles created by Gulamhuissen, it can be seen that effective professional development can help develop different competencies in the design and implementation of content, strategies, use of technologies, and other elements of continuous learning improvement professional learning
As teachers, we must talk to our students about taking responsibility for improving their practice. See setbacks and feedback as an opportunity to learn and develop your skills. They actively seek learning opportunities and new challenges. They have positive expectations to achieve success in GROWTH MINDSET.
The importance of the growth mindset is that we reconsider our approach to challenges and stay motivated to improve our skills. Instead of thinking, "I can't do this," let's think, "I can't do this yet."
References
Duckworth, A. L. [TED]. (2013, May 9). Grit: The power of passion and perseverance [Video file].
Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H14bBuluwB8&t=5s
Dweck, C. S. (2006). Mindset: The new psychology of success. New York: Random House.
Gerstein, J. (2015, September 04). Is "have a growth mindset" the new "just say no."
Retrieved from
Kohn, A. (2017, July 31). The "mindset" mindset. Retrieved from https://www.alfiekohn.org/article/mindset/
Whitman, G. (2014, August 06). The power of yet. Retrieved from https://www.edutopia.org/discussion/power76
